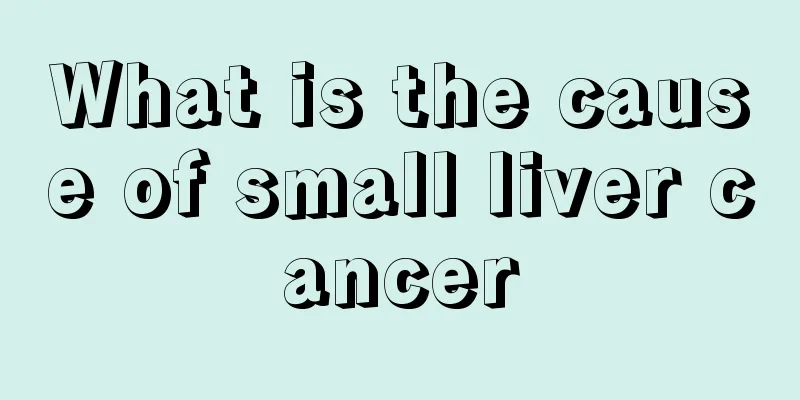The process of enterohepatic circulation

|
Enterohepatic circulation refers to the process and phenomenon that drugs pass through bile, then enter the intestine, are reabsorbed in the intestine, and then return to the liver through the portal vein. In other words, this method is used to promote the bile excretion of drugs. The significance of enterohepatic circulation determines the effect of drug excretion from bile, which can play a good role in preventing drugs from staying in the human body for too long and avoiding the problem of drug side effects. Enterohepatic circulation process 1. Chemical Cycle This phenomenon mainly occurs in drugs excreted through bile. Some prototype drugs excreted into the intestine through bile, such as strophanthus glycoside G, have high polarity and can rarely be absorbed from the intestine, and most of them are excreted through feces. Some drugs, such as chloramphenicol and phenolphthalein, become more water-soluble after combining with glucuronic acid in the liver, and are secreted into the bile and excreted into the intestines. They are hydrolyzed by intestinal bacterial enzymes to release the original drug, which is then absorbed by the intestines into the liver. Animal experiments have shown that antimicrobial drugs can reduce the enterohepatic circulation of certain drugs by inhibiting intestinal bacteria. The significance of enterohepatic circulation is determined by the excretion rate of drugs in bile. When drugs are absorbed, their excretion is increased. When the amount of bile excretion is large, the enterohepatic circulation can prolong the duration of drug action. If the enterohepatic circulation of the drug can be blocked, the excretion of the drug can be accelerated. If digitoxin poisoning occurs, taking cholestyramine can bind to it in the intestine and block its reabsorption. 2. Biological Cycle The excretion of drugs and their metabolites through bile is often an active process, and there are three active excretion pathways: acidic, alkaline and neutral. Certain drugs, especially those excreted through bile, can be partially reabsorbed through the intestinal epithelial cells after being discharged into the duodenum through bile. This is manifested in pharmacokinetic terms as a double peak in the drug-time curve and in pharmacodynamic terms as a significantly prolonged effect of the drug. Some conjugated metabolites are excreted into the intestine via bile, where they are hydrolyzed to release the parent drug, which is then reabsorbed to form an enterohepatic circulation[2]. 26% of digitoxin is excreted into the intestine via bile to form enterohepatic circulation, which is only one of the reasons for the long-lasting effect of the drug. Drugs excreted through breast milk, such as morphine, atropine, and ergot alkaloids, may cause poisoning in infants [2]. Overview The excretion of drugs in the body is mainly carried out through channels such as the kidneys, bile and mammary glands. Drugs are transformed by the liver and can be secreted into the bile as metabolites or unchanged, and discharged into the duodenum through the common bile duct. Part of them is reabsorbed by the small intestine, returns to the liver through the portal vein, and is then discharged into the intestinal cavity through the bile. This cycle repeats itself, forming the enterohepatic circulation. The significance of enterohepatic circulation is determined by the excretion rate of the drug in bile. When the amount of bile excretion is large, the enterohepatic circulation can prolong the duration of drug action. If the enterohepatic circulation of the drug can be blocked, the excretion of the drug can be accelerated. |
<<: What are the best ways to treat vitiligo
>>: What is the treatment for epilepsy
Recommend
What are the early symptoms of ovarian tumors
We may still not know much about ovarian tumors. ...
Patients with bedsores should be cared for in this way
Bedsores are ulcers on the skin caused by long-te...
Repairing scars left by surgery
In daily life, the probability of disease occurre...
Fifteen small habits to keep away from diseases
1. Drink plenty of water Water not only saves peo...
How long after a normal birth can I wear high heels
Every woman has high heels in her shoe cabinet. H...
Asperger's syndrome
Do you know Asperger's syndrome? It is a very...
Do you know the early symptoms of lung cancer? Pay attention to the six early symptoms of lung cancer
Lung cancer is now a very common disease in life....
The five most common symptoms of mid-stage lung cancer
Lung cancer is the most common primary lung malig...
Can you still eat rice if it has worms?
When it comes to rice, many people are familiar w...
Can gout be treated by soaking feet in hot water?
We all know that if we are very tired at work, we...
What is the cause of gallbladder cancer in the elderly?
Gallbladder cancer has a particularly high mortal...
Four unexpected uses for eggshells!
1. Clean clothes Most people have a headache clea...
How to Treat Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
How to treat esophageal adenocarcinoma? Although ...
A brief analysis on how to scientifically care for patients with bladder cancer
According to medical statistics in recent years, ...
What should I eat if I have kidney deficiency and insufficient qi and blood? 6 kinds of food to help women replenish qi and blood
In daily life, many female friends will have symp...