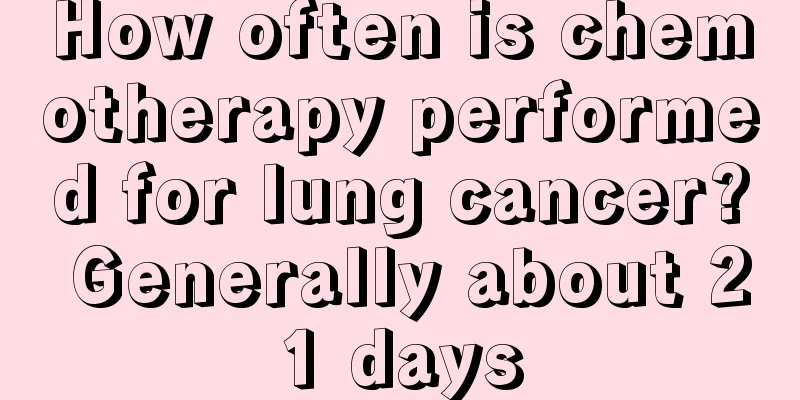What is the normal value of urea nitrogen and creatinine?

|
To determine whether kidney function is normal, we need to understand the normal range of urea nitrogen and creatinine. When urea nitrogen exceeds normal values, everyone needs to be aware that there is a high probability that there is a problem with the kidneys. When the body experiences symptoms such as edema, fatigue, etc., especially when the skin on the ankle is dimpled when pressed, go to the hospital as soon as possible to check the normal values of urea nitrogen and creatinine. Under normal circumstances, the ratio of blood urea nitrogen to creatinine (urea nitrogen/Scr) is about 10. A high-protein diet, high catabolic state, dehydration, renal ischemia, insufficient blood volume and certain acute glomerulonephritis can increase the ratio, even to 20-30. A low-protein diet and liver disease often lower the ratio, which is called hypoazotemia. What is the normal value of urea nitrogen? Generally speaking, the fasting urea nitrogen of a normal adult is 3.2-7.1mmol/L (9-20mg/d1). Reference value of urease indophenol method: M (male): 2.89-7.85mmol/L L (female): 2.78-7.32mml/L; reference value of urease-sodium reagent colorimetric method: 3.21-6.07mmoI/L The normal value of urea nitrogen varies slightly in different places. It is generally believed that the normal value of urea nitrogen is 2.86-7.14mmol/L. Various renal parenchymal lesions, such as glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, acute and chronic renal failure, intrarenal space-occupying and destructive lesions can all increase blood urea nitrogen. Multiple extra-renal factors can also cause increased blood urea nitrogen. If the extra-renal factors can be ruled out, urea nitrogen of 21.4mmol/L (60mg/d1) is one of the diagnostic indicators of uremia. The level of urea nitrogen is easily affected by diet and renal blood flow. If there are protein decomposition factors - infection, intestinal bleeding, hyperthyroidism, etc., the urea nitrogen can be increased. When the glomerular filtration rate drops to 1/2-1/3 of the normal level, urea nitrogen gradually increases. Under normal circumstances, the ratio of blood urea nitrogen to blood creatinine is 10:1. The reasons for the high ratio include gastrointestinal bleeding, hemolysis, heart failure and enhanced tissue decomposition (burns, high fever, cortical hormone treatment, etc.), which are mostly caused by prerenal factors. A decreased ratio is seen in insufficient protein intake, severe liver and kidney dysfunction, etc. Urea nitrogen concentration is affected by many factors, which can be divided into two aspects: physiological factors and pathological factors. 1. Physiological factors: A high-protein diet can cause an increase in serum urea nitrogen concentration, which is 2-3 mg/dL higher in men than in women on average. 2. Pathological factors: a. Prerenal: severe vomiting, pyloric obstruction, massive gastrointestinal bleeding, intestinal obstruction and long-term diarrhea, etc. b. Renal: acute glomerulonephritis, chronic nephritis, chronic pyelonephritis, late stage renal disease, renal failure and toxic nephritis. c. Post-renal diseases: prostate enlargement, urinary tract stones, urethral stenosis, urinary tract compression caused by bladder tumors, etc. |
<<: Early symptoms of hepatitis
>>: What should I do if my toe joints hurt?
Recommend
How to diagnose kidney cancer in the elderly
The cause of kidney cancer in the elderly is stil...
Can sesame paste be eaten with milk? Can sesame paste be drunk with milk?
Many people are very concerned about what they sh...
It takes several years after thyroid cancer surgery to pass the critical period
Thyroid cancer is a malignant tumor that originat...
Compound Heparin Sodium Allantoin Gel
In our daily life, many people will have scars on...
How to choose rice safely
Food safety has become a topic of great concern i...
What is the cause of stomach fire?
The term stomach fire is very common in tradition...
The harm of washing your face with cold water for a long time
Many people are not familiar with the harm of was...
What does Grain in Ear mean and when does it occur?
Among the songs about the twenty-four solar terms...
Polycystic ovary syndrome diet
The ovaries are an important organ in the female ...
What are the hazards of sulfuric acid to the human body
Sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive substance and...
What to do if there is a four-legged snake at home
The tetrapod is also what we often call a lizard....
Which hospital is good for treating advanced bone cancer
Which hospital is the best for treating advanced ...
What is the pain inside my arm
The limbs are the parts we use most frequently, a...
How to relieve liver cancer pain? Diet recipes for liver cancer patients
Liver cancer is a common type of malignant tumor ...
It turns out that Kapok soup has these magical effects
Now is the season when kapok flowers bloom. This ...