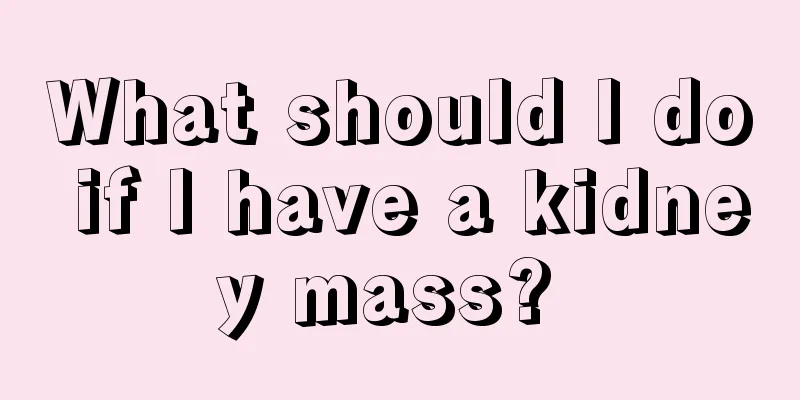Classification of esophageal atresia

|
The esophagus is an important passage for people to eat food. If esophageal atresia occurs, the serious harm is self-evident. Esophageal atresia is a congenital disease with a low incidence rate, but once a child has esophageal atresia, parents should take surgical treatment in time to avoid delaying the disease. At the same time, there are many different types of esophageal atresia. Today's article will explain to parents the classification of esophageal atresia problems. Classification Congenital esophageal atresia can be divided into five types according to the location of esophageal atresia and whether there is esophageal tracheal fistula. 1. Type I The proximal and distal esophagus are both blind-ended and do not connect to the trachea, and there is no esophageal-tracheal fistula. This type accounts for 7.7%. 2. Type II The proximal part of the esophagus enters the posterior wall of the trachea, forming an esophageal tracheal fistula, and the distal end is a blind end. This type is rare, accounting for about 0.8%. 3. Type III The proximal part of the esophagus is blind, and the distal part connects to the posterior wall of the trachea, forming an esophageal tracheal fistula. The types are further divided according to the distance between the two sections of the esophagus. If the distance is more than 2 cm, it is type IIIA; if it is less than 2 cm, it is type IIIB. Type IIIA esophageal anastomosis is quite difficult, while type IIIB esophageal anastomosis is relatively easy. According to Holder statistics, this type is the most common, accounting for about 86.5%. 4. Type IV The proximal and distal esophagus were connected to the posterior wall of the trachea, forming two tracheoesophageal fistulas. This type is also rare, accounting for 0.7%. 5. Type V The esophageal cavity is patent and without atresia, but the anterior wall of the esophagus is connected with the posterior wall of the trachea, forming an esophageal tracheal fistula, accounting for 4.2%. Clinical manifestations 1. The saliva cannot be swallowed and flows back into the mouth, resulting in drooling and foaming at the mouth after birth. 2. During each breastfeeding, the breast milk of type I and type III patients cannot be sent to the stomach and overflows into the respiratory tract; in type II, IV and V cases, the breast milk directly enters the trachea, causing choking, vomiting, difficulty breathing, cyanosis, and prone to aspiration pneumonia. In type I and type IV cases where there is an esophageal tracheal fistula between the lower esophagus and the trachea, respiratory air can enter the gastrointestinal tract through the fistula, causing abdominal distension. At the same time, gastric juice can also flow back into the respiratory tract through the esophageal tracheal fistula, causing aspiration pneumonia, presenting with fever and shortness of breath. 3. Because food cannot enter the gastrointestinal tract, the sick infant becomes dehydrated and emaciated. If not treated promptly, he or she may die from lung inflammation and severe dehydration within a few days. Physical examination often reveals signs of dehydration, with accumulation of saliva in the mouth. In patients with pneumonia, rales can be heard in the lungs, and percussion of the inflamed area is dull. examine 1. Esophagoscopy: An esophagoscope is inserted through the mouth or nasal cavity. It is blocked at the blind end of the upper esophagus and cannot pass into the stomach, or a closed esophagus may be seen. 2. Place a catheter through the mouth or nose, and inject a small amount of water-soluble iodine contrast agent through the catheter to show the location and length of the blind end of the upper esophagus, and determine whether there is a fistula between the upper esophagus and the trachea. Abdominal X-ray examination revealed gas in the gastrointestinal tract, indicating that the lower esophagus was connected to the trachea. Avoid using barium when performing esophageal radiography to avoid barium lung. Generally, water-soluble iodine can be used in small amounts. The contrast agent must be slowly injected into the blind end through the catheter. After taking the film, the contrast agent should be aspirated immediately to prevent pneumonia. treat If congenital esophageal atresia is not treated, death will occur within a few days of birth. Therefore, surgery should be performed as soon as possible after a clear diagnosis to correct the deformity. Before surgery, attention should be paid to adequate fluid replacement, correction of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance; prevention and treatment of aspiration pneumonia; administration of antibiotics; and maintenance of normal body temperature. Placing the child in a semi-sitting position can reduce the risk of gastric juice overflowing into the respiratory tract. Place a thin catheter in the upper esophageal cavity to continuously apply negative pressure or frequently suction oral secretions to prevent or reduce the amount of oral secretions being inhaled into the lungs. In cases of lung inflammation or atelectasis, ventilation function needs to be maintained and oxygen inhalation should be given. prevention Surgery is the fundamental measure for the treatment of this disease. In terms of prevention, the main thing is to try to achieve early detection, early diagnosis, and early treatment. If a newborn baby has excessive saliva and needs to be suctioned frequently, you should be highly alert to the possibility of this disease. At this time, the so-called "diagnostic feeding" should be avoided, and esophageal intubation should be performed to avoid the occurrence of pneumonia and to make a clear diagnosis as soon as possible. |
<<: Esophagus hurts when swallowing
>>: What's the matter with eyebrow hair falling out
Recommend
Urine protein positive 2+
Urine protein positive 2+ is the main indicator i...
Surgical treatment of colorectal cancer
In recent years, the incidence of colorectal canc...
What exactly is bone cancer?
Bone cancer is a cancer that occurs in bones or t...
What color is the pulmonary effusion caused by lung cancer?
The pulmonary effusion caused by lung cancer can ...
Postoperative care after laryngeal cancer resection
What are the postoperative care for laryngeal can...
Preparation and efficacy of Eucommia ulmoides flower tea
People who often study traditional Chinese medici...
Why does liver cancer cause shoulder pain? Which parts of the body will have abnormalities after liver cancer?
When it comes to liver cancer, the first thing th...
Types of Rhinoplasty
Many women choose larger beauty salons when they ...
Symptoms of appendix fecal stone pain
Appendicitis is a relatively common disease. Afte...
How to use Chinese medicine to treat nasopharyngeal carcinoma
How to use Chinese medicine to treat nasopharynge...
Symptoms of chronic urethritis, there are so many dangers
Chronic urethritis is extremely common in life. C...
Thyroid cancer resection, TSH index range control
After thyroid cancer surgery, patients need to co...
How to effectively prevent lung cancer? Try these 3 methods to prevent lung cancer
For diseases, the measures we should take are pre...
How long can I sleep after a meal?
I believe that for many friends, the happiest thi...
Introduction to the best way to kill mosquitoes
Summer is coming, and everyone knows that the mos...