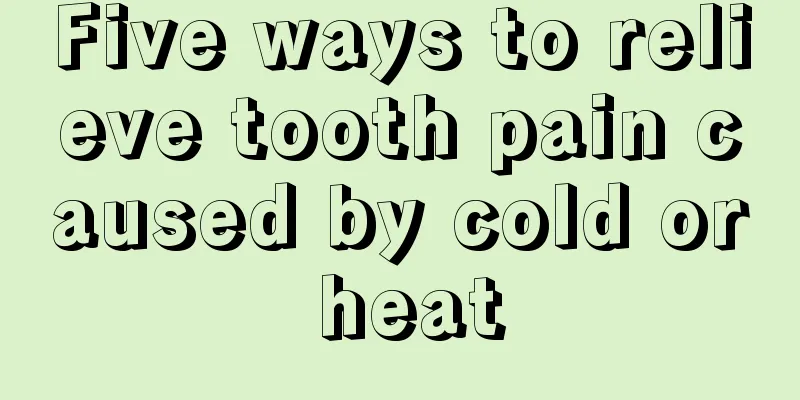
The basic skeleton of the cell membrane

|
Humans are made up of cells, and many living things in the world are made up of cells. Plants have plant cells and human cells. The structure of a cell has a cell membrane, a nucleus, and cytoplasm, etc. Plants also have chloroplasts, and human cells also contain mitochondria, etc. The cell membrane is the outermost semipermeable membrane of the cell. Let’s take a look at the basic skeleton of the cell membrane. The cell membrane is an elastic, semipermeable membrane mainly composed of phospholipids with a thickness of 8 to 10 nm. For animal cells, the outer side of the membrane is in contact with the external environment. Its main functions are to selectively exchange substances, absorb nutrients, excrete metabolic waste, and secrete and transport proteins. Membrane lipids are mainly composed of phospholipids, cholesterol and a small amount of glycolipids. In the membrane lipids of most cells, phospholipids account for more than 70% of the total, cholesterol does not exceed 30%, and glycolipids do not exceed 10%. Phospholipids can be divided into two categories: phosphoglycerides and sphingomyelin (SM). Glycerol phospholipids mainly include phosphatidylcholine (phosphatidylcholine, PC), followed by phosphatidylserine (phosphalidylserine, PS) and phosphatidylethanolamine (cephalin) (phosphatidylethanolamine, PE), and the least abundant is phosphatidylinositol (phosphatidylinosital, PI). Phospholipids, cholesterol and glycolipids are all amphiphilic molecules. Hydrophilic groups such as the phosphate and alkali groups in phospholipid molecules, the hydroxyl groups in cholesterol molecules, and the sugar chains in glycolipid molecules form the hydrophilic ends of their respective molecules, while the other ends of the molecules are hydrophobic fatty acid hydrocarbon chains. These molecules exist in the plasma membrane in the form of a lipid bilayer, with the hydrophilic ends facing the extracellular fluid or cytoplasm and the hydrophobic fatty acid hydrocarbon chains facing each other, forming a hydrophobic region inside the membrane. The lipid composition of the membrane lipid bilayer is asymmetric. Amino acid-containing phospholipids (phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylinositol) are mainly distributed in the inner layer of the membrane near the cytoplasm, while most and all of the phosphatidylcholine glycolipids are distributed in the outer layer of the membrane. Membrane Protein There are two types of proteins: intrinsic proteins and extrinsic proteins. Intrinsic proteins are covalently bound to the hydrophobic part of phospholipids with their hydrophobic parts, and both ends are polar, penetrating the inside and outside of the membrane; extrinsic proteins are bound to the outer ends of intrinsic proteins or to the hydrophilic heads of phospholipid molecules with non-covalent bonds. Such as carriers, specific receptors, enzymes, and surface antigens. 20% to 30% of surface proteins (peripheral proteins) bind to lipids on both sides of the membrane with charged amino acids or groups - polar groups; 70% to 80% of bound proteins (intrinsic proteins) bind to lipid molecules through one or several hydrophobic α-helices (formed by the absorption of 20 to 30 hydrophobic amino acids, with 3.6 amino acid residues per turn, equivalent to the thickness of the membrane. Adjacent α-helices are connected by straight-chain peptides on the inside and outside of the membrane), that is, the hydrophobic hydroxyls inside the membrane. Theoretically, proteins embedded in the lipid layer can float and shift laterally, so they should be randomly distributed; but in reality, they have a regional distribution (which may be related to the confinement of certain protein molecules by the cytoskeleton on the inner side of the membrane) in order to realize their special functions: the exchange of matter, energy and information between cells and the environment. (Frye and Edidin in 1970 used red-emitting alkaline cinnamaldehyde to label human cells and cultured mouse cells cultured in vitro with green-emitting fluorescein-labeled membrane protein antibodies, and then allowed them to fuse. After 40 minutes at 37°C, they became evenly distributed. Photobleaching fluorescence recovery method, micro-area monitoring) There are two main types of transport proteins on the cell membrane: carrier proteins and channel proteins. Carrier proteins, also known as carriers, permeases and transporters, can bind to specific solutes and transfer the bound solutes to the other side of the membrane through changes in their own conformation. Some carrier proteins require energy to drive, such as various ATP-driven ion pumps; others do not require energy and transport substances by assisted diffusion, such as valinase. Channel proteins have a weak binding to the substances they transport and can form hydrophilic channels that allow specific solutes to pass through when the channels are open. All channel proteins transport solutes by assisted diffusion. Membrane sugar Membrane sugars and sugar coatings: glycoproteins, glycolipids Cell membrane carbohydrates are mainly oligosaccharide chains and polysaccharide chains, which are covalently bound to membrane lipids or proteins to form glycolipids and glycoproteins; most of these sugar chains are exposed on the outside (non-cytoplasmic) side of the membrane. (Polysaccharide-protein complex, cell coat) The specificity of monosaccharide arrangement serves as the "marker, antenna" of cells or proteins - antigenic determinant (recognizable, binding to transmitters, hormones, etc. The oligosaccharide chains on ABO blood type substances, namely sphingosine, are different. 131AA+100 sugar residues). |
<<: Characteristics of cell membrane structure
>>: How many dried mulberries do you need to soak in water in a day
Recommend
There is a hole in the tooth with a bad smell and bleeding
When we interact with others, it would be very em...
Patients with cervical cancer should take good care of themselves before treatment
Cervical cancer is the most common malignant tumo...
Nursing points for patients with bone cancer
Everyone should know that bone cancer is a very s...
My right elbow hurts, what's wrong?
If you feel pain in your right arm, there are man...
Will the swelling of the lymph nodes go down after anti-inflammation?
As we all know, there is a lymphatic system in ou...
What are the early symptoms of lymphoma and how to treat it
What are the early symptoms of lymphoma? How to t...
How to prevent ovarian tumors
Ovarian malignant tumors can bother many friends ...
Can kidney cancer be prevented?
The answer to the question of whether kidney canc...
What is the reason for bitter lips
Sometimes when we wake up in the morning, our lip...
It turns out that these two types of Chinese medicine can be used for cerebral infarction
Cerebral infarction is a common disease in daily ...
Can nasopharyngeal cancer be treated directly with surgery?
Can nasopharyngeal cancer be treated directly wit...
What are the benefits of soaking your feet in ginger slices regularly
Soaking your feet is a lifestyle habit that has a...
Use salt water to reduce inflammation of swollen gums
Swollen gums are a common problem in life. There ...
What are the hydrating sleeping masks
Facial masks are a must-have item for modern wome...
What are the examination methods for kidney cancer
In daily life, we need to pay attention to the oc...