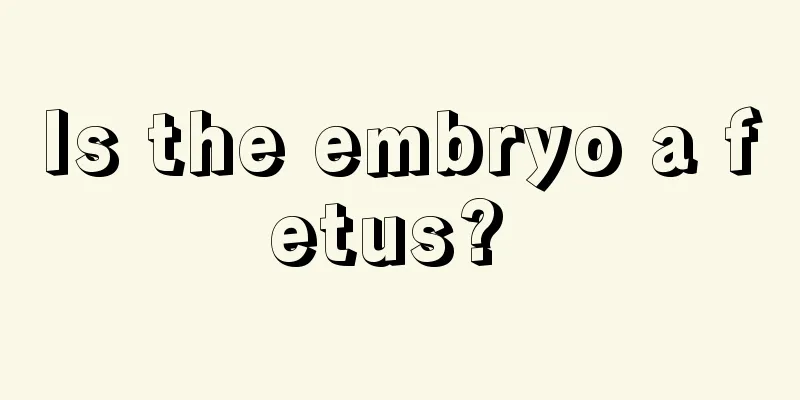
X-ray barium meal examination findings of advanced gastric cancer

|
The general classification of advanced gastric cancer is generally based on the Borrmann classification, which includes Borrmann type I, Borrmann type II, Borrmann type III and Borrmann type IV. The X-ray findings of each type are described as follows: 1. Borrmann type I (polyp type or mushroom type) The tumor grows into the cavity, showing irregular filling defects. Double contrast phase and moderate pressure phase can more specifically show the beginning of the mass and the abnormal characteristics of its surface structure. Because the local mucosa is destroyed and disappears, its surface is often rough and uneven, like cauliflower, with small ulcer niches and defects. The mucosal patterns adjacent to the defect area are suddenly interrupted, and the local gastric wall where the raised lesion is attached is stiff, resulting in a clear boundary between the lesion area and the normal area. 2. Borrmann type II (ulcerative type) The mass grows in a localized manner, with a large ulcer in the center and a prominent bulge at the edge of the ulcer, like a crater; ulcerative gastric cancer mainly occurs above the mass, with the niche located within the stomach contour, irregular in shape, and the lateral edge showing a typical "half-moon sign". The outer edge is straight, the inner edge is irregular and has multiple sharp corners, and the niche is surrounded by a transparent band, namely the "ring embankment sign", which is uneven in width and has an irregular and sharp outline. 3. Borrmann type III (ulcer infiltrative type) The bulge with nodular edges infiltrates to the surrounding area. The mucosal folds are destroyed, disappeared or interrupted, and the adjacent gastric mucosa is stiff and peristalsis disappears. It is difficult to distinguish between type II and type III in X-ray manifestations. Both can show a half-moon sign, while the mass of type III grows diffusely. Although there is also ulceration in the center, the bulge around it is relatively flat. 4. Borrmann type IV (diffuse infiltrative type)Cancerous tissue diffuses and spreads in the stomach wall, affecting a wide area. X-rays show that part or the entire stomach cavity becomes stiff and shrunken, with no peristalsis, and looks like a leathery cyst. |
<<: Four common types of laryngeal cancer
>>: Common complications after pancreatic cancer surgery
Recommend
What should you pay attention to when recovering from nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Radiotherapy is the first choice for NPC patients...
Is hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy good?
The abdominal cavity is very important to our bod...
What to do if you don't eat and have a headache in the late stage of brain cancer
What should I do if I don't eat and have a he...
How to whip the butter so it won't melt
Many people like to bake, but when baking, they u...
Six foods that can prevent prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common maligna...
How long can a patient with advanced brain cancer live in coma
Intracranial tumors, also known as brain tumors, ...
Enlarged thyroid gland on the right side of the neck
For goiter, it is usually very important to stren...
Which electric heater is better
In winter, many people will choose some electric ...
How do we distinguish the authenticity of Pueraria powder
I believe everyone is familiar with Pueraria loba...
What are the functions and effects of ginger and white vinegar?
Ginger and white vinegar are two ingredients that...
Was there severe vaginal bleeding last night?
Whether the vaginal bleeding last night is severe...
Is the foot massage mat useful?
Foot massage pads have become a popular product i...
What are the symptoms and characteristics of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a very common disease. In rece...
Introduction to lesions of primitive squamous epithelium of the cervix
I believe that many female compatriots are very c...
How to relieve mild concussion
A head hit often leads to a concussion. If it is ...