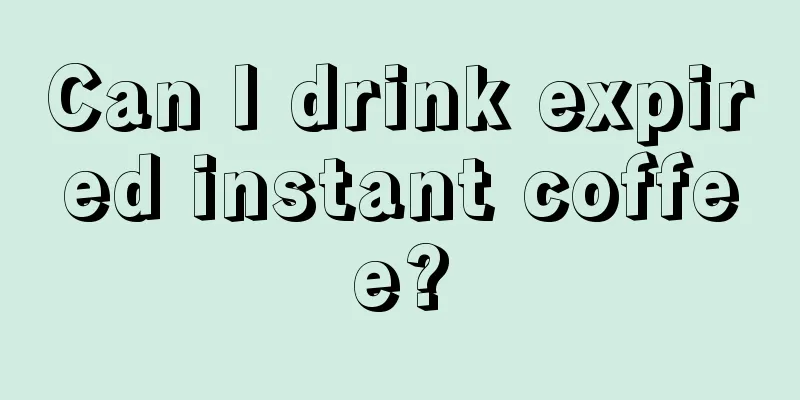The one that belongs to the brain skull is

|
Although we often hear the term skull in our daily lives, most people are not very clear about the main components of the human skull. The skull is the most important bone in the human body. If it is injured, the harm is self-evident. Therefore, we must pay attention to the protection of the skull. What are the main bone parts of the human skull? The cerebral cranium is composed of eight bones, including the paired temporal and parietal bones, and the unpaired frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and occipital bones. They enclose the cranial cavity. The top of the cranial cavity is the dome-shaped calvaria, which is composed of the frontal, occipital and parietal bones. The floor of the cranial cavity is formed by the sphenoid, occipital, temporal, frontal, and ethmoid bones. Only a small part of the ethmoid bone is involved in the brain skull, and the rest constitutes the facial skull. Frontal bone Located in the front and upper part of the skull, it is divided into the frontal, orbital and nasal parts. The frontal scales are shell-shaped, and the cavity between the nose and the orbit is called the frontal sinus; The orbital part is a thin, flat bone plate that extends backward and constitutes the supraorbital wall; the nose is located between the two orbital parts, in the shape of a horseshoe, with the notch being the ethmoid notch. Ethmoid bone Located between the two orbits, in front of the sphenoid body, it constitutes the upper and lateral walls of the nasal cavity. The ethmoid bone is in the shape of a scarf in the coronal plane and is divided into the ethmoid plate, vertical plate and ethmoid labyrinth. The cribriform plate is a porous horizontal bone plate that forms the roof of the nasal cavity. The bony ridge extending upward from the front part of the plate is called the comb; the vertical plate hangs down from the midline of the cribriform plate, located in the mid-sagittal position, and forms the upper part of the bony nasal septum; the ethmoid labyrinth is located on both sides of the vertical plate, and the small cavity surrounded by thin bone sheets is called the ethmoid sinus. There are two small curled bones on the medial wall of the labyrinth, the superior turbinate and the middle turbinate. The lateral wall of the labyrinth is extremely thin in bone and constitutes the medial wall of the orbit, called the orbital plate. Sphenoid bone Located in the center of the skull base, it is shaped like a butterfly with its wings spread, and consists of four parts: the sphenoid body, the greater wing, the lesser wing, and the pterygoid process. The sphenoid body is a cubic bone block in the middle part, which contains the sphenoid sinus. The sinus is divided into left and right halves and opens forward into the sphenoethmoid recess. The body surface is saddle-shaped, called the sella turcica, and the central depression is the hypophysial fossa. The greater wing extends from the body to both sides and is divided into the concave cerebral surface, the anteromedial orbital surface, and the outer and inferior temporal surface. The temporal surface is divided into upper and lower parts by the infratemporal ridge: the upper part is part of the temporal fossa, and the lower part constitutes the top of the infratemporal fossa. From front to back, there are three foramen rotundum, foramen ovale and foramen spinosum at the root of the greater wing, through which nerves and blood vessels pass respectively. The lesser wing is a triangular thin plate that originates from the anterior and superior part of the sphenoid body. It is the posterior part of the anterior cranial fossa above and the posterior part of the supraorbital wall below. The optic canal is located at the junction of the wing and the body. The fissure between the lesser and greater wing is the superior orbital fissure. The pterygoid process extends downward from the junction of the body and the wing and is composed of an inner plate and an outer plate. The thin tube that runs through the root in the sagittal direction is called the pterygoid canal, which leads forward into the pterygopalatine fossa. Temporal bone Participates in the formation of the skull base and the side walls of the cranial cavity, and is divided into the squamous part, the tympanic part, and the petrous part with the external auditory meatus as the center: Squamous Located in the upper and anterior part of the external auditory meatus, it is scaly in shape. The inner surface has the pressure marks of the gyrus and the groove of the middle meningeal artery; the outer surface is smooth, with a zygomatic process extending forward in the anterior and inferior part, which forms the zygomatic arch with the temporal process of the zygomatic bone. The deep pit below the root of the zygomatic process is the mandibular fossa, and the anterior edge of the fossa is relatively protruding, called the articular tubercle. Drum Located behind the mandibular fossa, it is a curved bone piece. Surrounds the external auditory canal from the front, bottom, and back. Iwabe It is in the shape of a triangular pyramid, with the tip pointing forward and inward facing the sphenoid body, and the base connected to the squamous part. The front faces the middle cranial fossa, with an arched bulge in the center. The thinner part on the outside of the bulge is called the tympanic membrane, and there is a smooth trigeminal nerve pressure mark near the tip. There is a hole in the middle of the back, the internal acoustic pore, which leads to the internal auditory canal. The bottom is uneven, with the external opening of the carotid canal in the center, which leads upward into the carotid canal. This canal first ascends vertically, then bends forward and inward, opening at the petrous apex, which is called the internal opening of the carotid canal. The deep fossa behind the orifice of the carotid artery is the jugular fossa, and the slender bony protrusion on the posterolateral side is the styloid process. Behind the external auditory meatus, the protrusion of the petrous part extending downward is called the mastoid process, which contains many cavities called mastoid cells. The small hole behind the root of the stylomastoid process is the stylomastoid foramen. Occipital bone Located at the lower back of the skull. There is a foramen magnum in the front and lower part, through which the occipital bone is divided into four parts. The front is the base, the back is the occipital scales, and the sides are the sides. There is an oval protrusion on the lower side called the occipital condyle, and the articular surface below the condyle is articulated with the superior articular surface of the atlas. Parietal bone Quadrilateral, located in the middle of the skull. |
<<: What does the skull include
Recommend
Late manifestations of bladder cancer symptoms
In the late stage of bladder cancer, symptoms may...
What are the symptoms of colorectal cancer
The symptoms of colorectal cancer vary depending ...
What are some small ways to lift your buttocks
Many people around us are already very outstandin...
Can stomach cancer be cured? There are four treatments
Whether gastric cancer can be cured is closely re...
Chinese herbal secret recipe for treating esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer is a malignant tumor that occur...
My waist suddenly hurts so much that I can't move
The waist is an important part of our body. I won...
How much does intervention for bladder cancer cost
Bladder cancer not only has a great impact on the...
What are the nursing methods for acne on the belly
When some pimples appear on our body, no matter w...
What are the signs of nasopharyngeal cancer and how to treat it
The earlier nasopharyngeal cancer is treated, the...
How to straighten bent legs_How to straighten bent legs
Summer is coming soon, and summer is the season f...
What are the materials of removable dentures
In our lives, more and more people are always tro...
What to do if bone cancer causes severe pain
What should I do if the pain from bone cancer is ...
What is the cause of pelvic pain
The pelvis is the area of the body located at t...
6 signs to help you find invisible cancer
Many people find out they have cancer when it is ...
Five early symptoms of gastric cancer How to treat gastric cancer
The five early symptoms of gastric cancer include...